Capacitor is a basic and one of the most important components in electronics.
Capacitors come in various types, each suited for specific applications. Here are some common types of capacitors:
Ceramic Capacitors: Widely used in electronic circuits for their small size and stability. They come in various temperature coefficients and voltage ratings.
Electrolytic Capacitors: Typically used for power supply filtering and energy storage due to their large capacitance values. They are polarized and have higher capacitance per unit volume compared to ceramic capacitors.
Tantalum Capacitors: Similar to electrolytic capacitors but offer better performance in terms of stability and reliability. They are also polarized and used in applications requiring high capacitance and low leakage current.
Film Capacitors: Known for their high precision, stability, and low loss. They are used in applications where a stable and reliable capacitor is required, such as in audio equipment and power electronics.
Supercapacitors (Ultracapacitors): Offer very high capacitance values and can store large amounts of energy. They are used in applications requiring rapid charge and discharge cycles, such as in energy storage systems and backup power supplies.
Mica Capacitors: Provide high precision and stability, often used in RF and microwave applications due to their low loss and high-frequency performance.
Polymer Capacitors: Similar to electrolytic capacitors but use a solid polymer electrolyte. They offer better performance in terms of ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) and stability.
Variable Capacitors: Allow adjustment of capacitance value, commonly used in tuning circuits for radios and other communication devices.
Each type of capacitor has its unique characteristics and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the application.
ESR:
ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) is an important characteristic of capacitors. In some applications like switching-mode power supplies (SMPS) this parameter plays a critical role to select the capacitor.
The capacitor model is shown below.
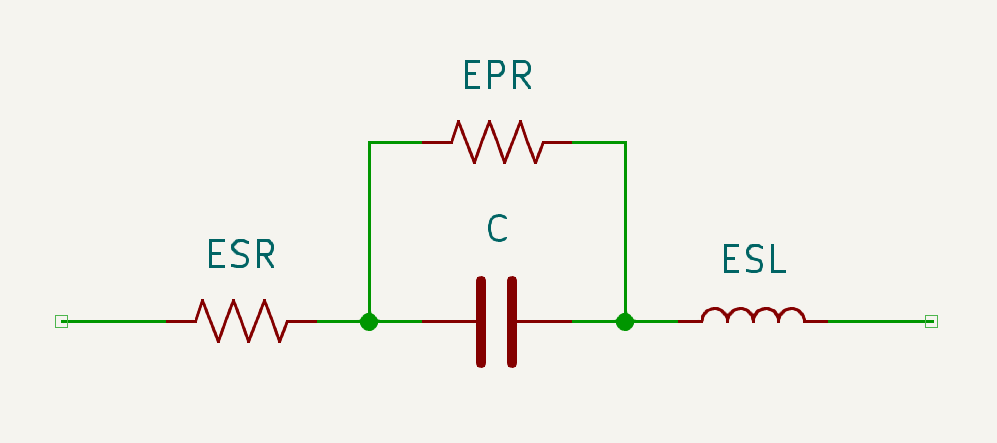
Some manufacturers produce capacitors specifically for low-ESR. The specifications of Low-ESR Series can be found in data sheets published by manufacturers. The table below shows some popular Low-ESR series of capacitors.
| Manufacturer | Series | Style | Technology | Low ESR down to [mΩ @ 20ºC / 100kHz |
| AVX | TCJ | Chip | Polymer aluminium | 10 |
| AVX | TCQ | Chip | Polymer aluminium | 25 |
| AVX | TCM | Chip | Polymer tantalum multi-anode | 6 |
| AVX | TPS | Chip | Tantalum | 25 |
| AVX | TPM | Chip | Tantalum | 12 |
| KEMET | A700 | Chip | Polymer aluminium | 4.5 |
| KEMET | A759 | Radial | Polymer aluminium | 12 |
| KEMET | A768 | SMD | Polymer aluminium | 15 |
| KEMET | T528 | Chip | Tantalum multi-anode | 4 |
| KEMET | T520/T530 | Chip | Tantalum multi-anode | 4 |
| Murata | ECAS | Chip | Polymer aluminium | 6 |
| Nichicon | GYB | Chip | Aluminium electrolytic | 20 |
| Nichicon | GYC | Chip | Aluminium electrolytic | 20 |
| Nichicon | PCH | Chip | Aluminium electrolytic | 13 |
| Nichicon | PCR | Chip | Aluminium electrolytic | 13 |
| Nichicon | UCM | Chip | Aluminium electrolytic | 50 |
| Nichicon | UCZ | Chip | Aluminium electrolytic | 32 |
| Panasonic | FN | SMD | Aluminium electrolytic | 80 |
| Panasonic | FT | SMD | Aluminium electrolytic | 60 |
| Panasonic | FS | Radial | Aluminium electrolytic | 12 |
| Panasonic | OS-CON™ | Chip | Polymer aluminium | 14 |
| Panasonic | SP-Cap | Chip | Polymer aluminium | 6 |
| Panasonic | ZA | SMD | Polymer hybrid | 20 |
| Panasonic | ZC | SMD | Polymer hybrid | 20 |
| Rubycon | ZLH | Radial | Aluminium electrolytic | 12 |
| Rubycon | PC-CON | Chip | Polymer aluminium | 4.5 |
| Vishay | 190 RTL | Radial | Aluminium electrolytic | 17 |
| Vishay | 170 RVZ | Radial | Aluminium electrolytic | 17 |